Selective Catalytic Reduction
Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) is changing the game when it comes to fighting air pollution from vehicles, industrial engines, and power plants. Instead of releasing harmful nitrogen oxides (NOx) into the air, SCR technology converts them into harmless nitrogen and water vapor. That means less smog, less acid rain, and cleaner air for everyone. With stricter environmental rules and growing pressure to cut emissions, industries need solutions that don’t hurt performance or break the bank—and SCR delivers exactly that: cleaner operations, better efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
What Is Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)?
In simple terms, SCR is an advanced emissions control technology that converts nitrogen oxides into nitrogen and water—both naturally found in the air—using a chemical reaction accelerated by a catalyst. Think of SCR as a powerful filter, but instead of trapping pollutants, it transforms them chemically.
SCR works by injecting a reductant—usually a urea-based Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) or ammonia—into hot exhaust gases. This combination reacts on a catalyst surface, with formulas like:
4NO+4NH3+O2=4N2+6H2O4NO+4NH3+O2=4N2+6H2O
or, when using urea:
4NO+2(NH2)2CO+O2=4N2+4H2O+2CO24NO+2(NH2)2CO+O2=4N2+4H2O+2CO2
The result? Up to 90% reduction in nitrogen oxides, dramatically lowering pollution without affecting engine function (kus-usa.com).
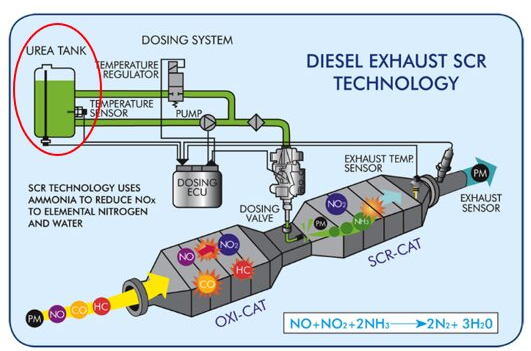
How SCR Technology Works and Its Benefits
SCR systems consist of:
- A dosing unit to inject DEF or ammonia,
- A catalytic converter inside the exhaust system,
- Sensors and controllers to optimize dosing and reaction.
As exhaust gases pass through the catalyst, harmful NOx molecules react with the reducing agent, breaking down into nitrogen and water vapor. This process happens at high temperatures (around 550°F to 750°F).
Benefits include:
- Significant NOx reduction (70%-95%) improving air quality
- Compliance with stringent emissions standards like Euro 6 and Tier 4 Final
- Applicability across vehicles from heavy trucks to marine engines
- No harmful by-products; just harmless nitrogen and water
Statistically, SCR technology has enabled up to a 95% decrease in NOx emissions from diesel engines, substantially helping industries meet environmental regulations and contribute to public health (kus-usa.com).
Real-World Uses of SCR
Today, SCR is the preferred technology for reducing nitrogen oxides in various sectors:
- Heavy-duty trucks and buses comply with emissions standards worldwide.
- Power plants install large SCR units to treat boiler exhaust gas.
- Shipping industries use SCR reactors for cleaner marine diesel engines.
- Industrial and municipal waste facilities utilize SCR to control pollution.
This technology’s adaptability ensures it remains key in achieving cleaner air goals across transportation and industrial landscapes.
Embrace SCR for a Sustainable Future
For businesses and industries aiming to reduce their environmental footprint, investing in Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) technology is a smart, proven solution. Whether upgrading fleets or industrial plants, SCR offers effective NOx reduction, regulatory compliance, and a cleaner environment.
Stay informed on the latest SCR advancements and partner with trusted DEF and emissions control experts at DEF & Oil Solutions.
Cleaner air begins with smarter choices—start leveraging SCR today to drive sustainability and performance forward.
FAQs
What is Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR)?
Selective Catalytic Reduction is a process that reduces nitrogen oxides in exhaust gases by injecting a urea-based fluid or ammonia, which reacts with the pollutants on a catalyst to form harmless nitrogen and water vapor.
How effective is Selective Catalytic Reduction?
SCR systems can reduce nitrogen oxide emissions by up to 90%, making them essential for meeting strict environmental standards for vehicles and industrial sources.
Why is SCR important?
SCR technology helps lower air pollution from nitrogen oxides, improving air quality, public health, and helping industries comply with environmental laws.

